To understand communication protocols we first need to understand digital systems. A digital system communicates a message in the form of binary information. This is a flow of digital pulses sent from one point to another creating a means of data transmission.

Serial communication is a widely used medium to transfer information between various equipment and peripherals. Data is in the form of sequential binary pulses. Binary can be represented in two states: a one (1) represents a logic high or “on” status and a zero (0) represents a logic low or “off” status.
The different modes of transmitting data over serial communication:
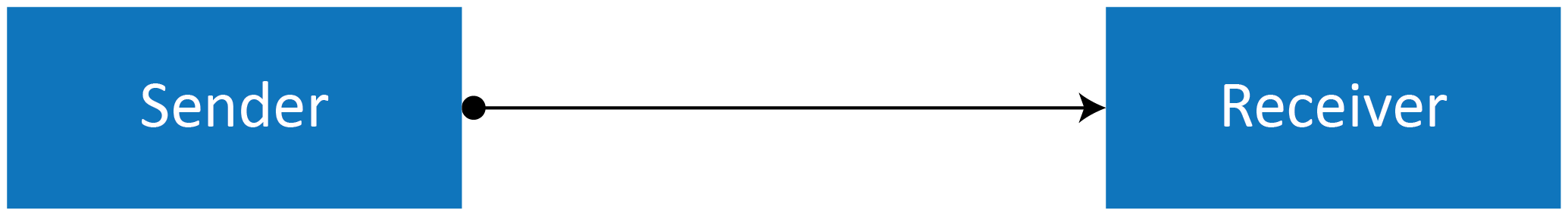
- Simplex transmission
This is a one-way communication method, with only one client present on the network. If a sender engages in transmission then a receiver is only able to accept information.
Examples: Radio and television transmission.
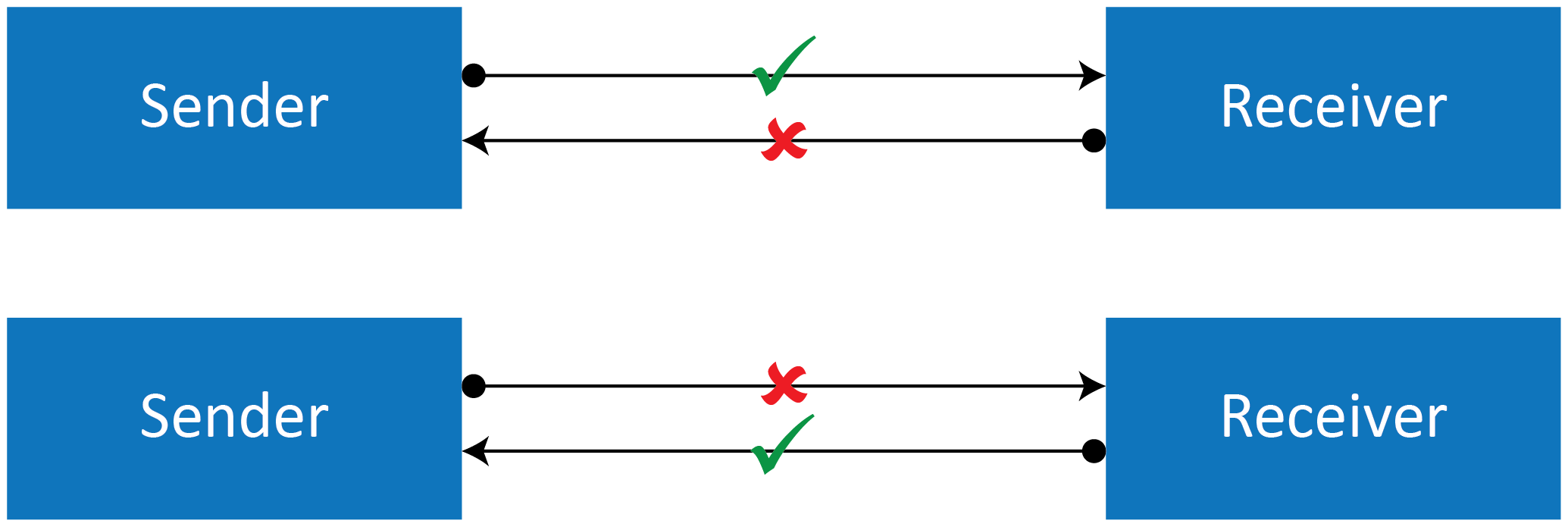
- Half Duplex:
This mode has both an active sender and a receiver, however, these can not be active at the same time. If a sender transmits information then a receiver will accept, but can not transmit and vice-versa.
A good example of this is PROFIBUS DP networks, these communicate over serial copper mediums (not exclusively) and when a controller device communicates to device stations, the device will stay silent until the controller has concluded the message transmission, once this is completed then the device station will respond with the requested information.
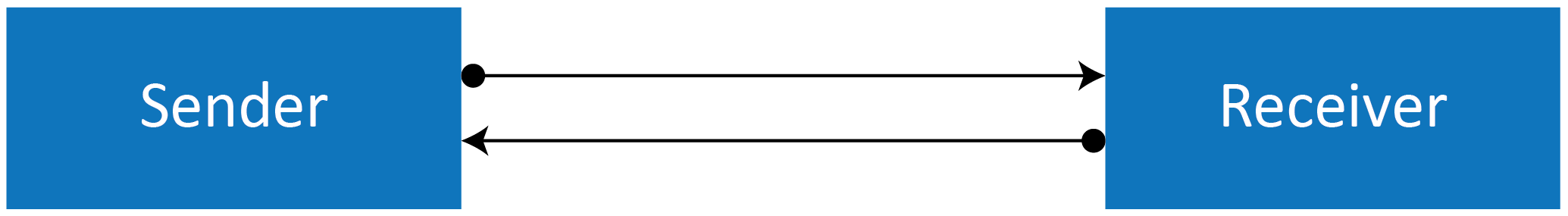
- Full Duplex mode
This mode is widely used when high-speed transmission is required in serial communication. Both the sender and receiver can communicate at the same time as there are dedicated cable cores for transmitting and receiving data. Transmission over RS232 utilises full duplex transmission methods.
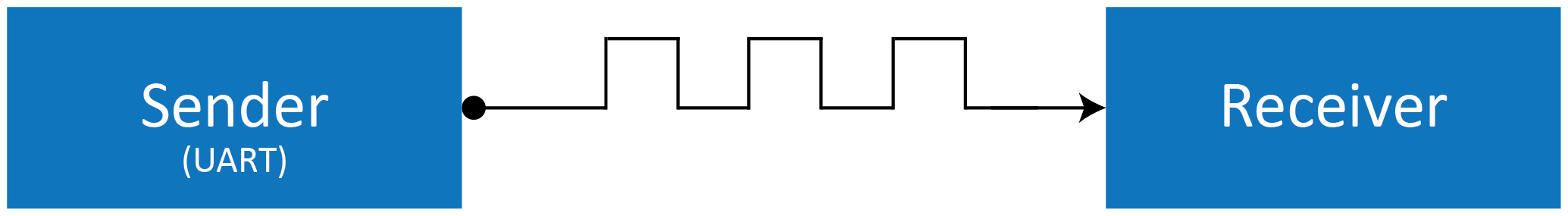
How does serial communication get created and generated?
Serial communication on a hardware level can be simply explained through the use of a microprocessor and a Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter (UART). The microprocessor composes information and sends this in the form of bytes to the UART, which then sends this information out in a series of bits.
The data sent out from the UART is classified as a serial frame and is arranged in a specific sequence. It comprises a start bit, some data bits and a stop bit.
Some important factors for the successful serial transmission of data:
Baud rate which is the speed at which data bits are transferred between the transmitter and the receiver, this speed needs to be configured the same for both nodes. The transfer speed is usually specified in bits per second. There are various standard baud rates: 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600 +. PROFIBUS can run up to 12582912 bps, which is very fast for a serial bus running over a copper medium.
Data bits are the number of bits composed into the serial message fame, usually 7 or 8. Parity is an error-checking bit used to make the message frame even or odd. The parity bit provides the receiver with a mechanism to determine if the frame has been corrupted or changed during transmission, for example by interference from high-voltage cabling running close to your serial data lines.
Some important factors for the successful use of the serial data systems
- Understanding the protocol
Protocols and standards are what make networks and devices work together successfully. Protocols have rules set in place to enable effective communication to occur. Attending training with a protocol expert can help to bring the blurred lines into focus. - Endianness
When designing computers and embedded devices, there are two different architectures for handling memory storage. They are called big-endian and little-endian. They refer to the order in which the bytes are stored in memory, i.e. The most significant bit is consumed first (big-endian), or the least significant bit is consumed first (little-endian). Windows NT was designed around little-endian architecture and was not designed to be compatible with big-endian because most programs are written with some dependency on little-endian. Some protocols however require a big-endian format e.g. PROFIBUS DP. - Data storage
There are various memory locations within a serial network, the common areas are input and output memory. Serial networks are used by several protocols and it is essential to note the data storage and bit transfer sizes allowable on these specific networks. Considerations for memory location, memory start address, data types and length are critical for the successful use and implementation of serial communication systems. - Checksum
Most serial protocols feature some way of verifying that the data has not been corrupted during transfer. A checksum is the result of running an algorithm on a piece of data, also known as the cryptographic hash function. Comparing the checksum data received with the algorithmic equivalent for that piece of data will determine if this data is genuine and can be used or if the data has errors and should be rejected. Checking for checksum errors on your serial networks, or CRC errors is a useful way of determining if there is some underlying fault that is reducing the network health and availability. Any errors should investigated and faults corrected.









